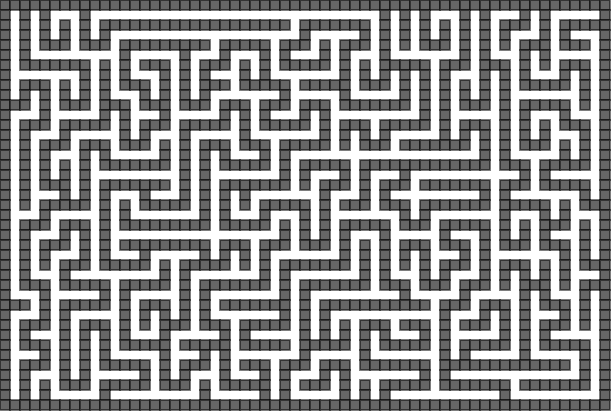
壁のばし法
実行例
ソースコード
TypeScript
解説/アルゴリズム
map = [];
for (let y = 0; y < tileHeight; y++) {
map[y] = [];
for (let x = 0; x < tileWidth; x++) {
if (x === 0 || x === tileWidth - 1 || y === 0 || y === tileHeight - 1) {
map[y][x] = CellType.Wall;
} else {
map[y][x] = CellType.Floor;
}
}
}
サイズが奇数 × 奇数の二次元配列を用意する。
配列の外側をすべて壁で埋めておく。

positions = [];
for (let y = 0; y < tileHeight; y += 2) {
positions.push({ x: 0, y });
positions.push({ x: tileWidth - 1, y });
}
for (let x = 0; x < tileWidth; x += 2) {
positions.push({ x, y: 0 });
positions.push({ x, y: tileHeight - 1 });
}
shuffle(positions);
縦横奇数番目の壁の位置をすべて取得し配列に格納する。
配列の要素をランダムに並び替えておく。
while (0 < positions.length) {
const next = positions.shift();
createWall(next.x, next.y);
}
function createWall(x: number, y: number): void {
const dirs = directions.slice();
shuffle(dirs);
for (const dir of dirs) {
const tx = x + dir.x;
const ty = y + dir.y;
const tx2 = x + dir.x * 2;
const ty2 = y + dir.y * 2;
if (
0 <= tx2 &&
tx2 < tileWidth &&
0 <= ty2 &&
ty2 < tileHeight &&
map[ty][tx] === CellType.Floor &&
map[ty2][tx2] === CellType.Floor
) {
map[ty][tx] = CellType.Wall;
map[ty2][tx2] = CellType.Wall;
positions.unshift({ x: tx2, y: ty2 });
positions.push({ x, y });
break;
}
}
}
下記処理を配列の中身が空になるまで繰り返す。
- 配列の先頭から要素(位置)を一つ取り出す。
- 取り出した位置から上下左右それぞれを見て、それらの方向の 1 マス先と 2 マス先が壁なら掘り進める。
- 掘り進めた 2 つ先の位置を配列の
先頭に登録。 - 取り出した位置を配列の
末尾に登録。 - 上下左右をチェックするループを強制的に抜ける。
例えば上下左右のうち、上に掘り進めそうなら、そのまま上の 2 マス先まで掘り進め、2 マス先の位置を配列の先頭に登録する。先頭に登録するのはこのすぐあとにそこからまたスタートしたいから。
上に掘り進んだ場合、まだ確認していない方向を見ずに上下左右ループを抜ける。
取り出した位置を末尾に登録しているので、後に他の方向をチェックできるから。
この処理はいわゆる深さ優先探索となる。

上記探索が終了すると迷路が完成する。
