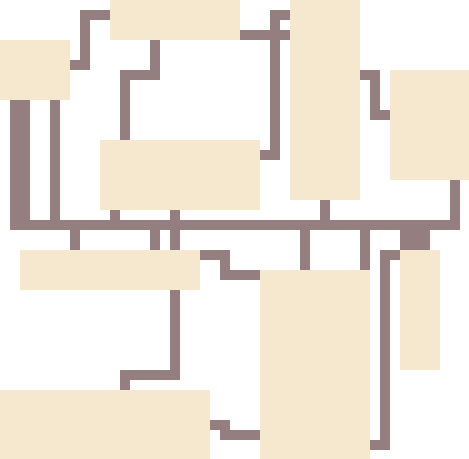
マップ生成3
実行結果
ソースコード
通路が一本道
rectangle.ts / mathutil.ts / app.ts
通路が複数
rectangle.ts / mathutil.ts / app.ts
解説/アルゴリズム
全体の流れ
- 用意した矩形を再帰的に分割を行い、幾つかの領域を作成する。
- 各領域の中に部屋を作る。
- 部屋同士を通路で繋ぐ。
矩形分割
// 領域の最低サイズ
const minPartitionSize = 8;
// 矩形を分割するには最低この値以上のサイズが必要(領域2つと通路1マス)
const splitRectSize = minPartitionSize * 2 + 1;
function splitRect(rect: Rectangle): Rectangle[] {
// 領域2つの最低サイズと通路用の1マス分が確保できなければ、これ以上分割をしない
if (r.height(rect) < splitRectSize || r.width(rect) < splitRectSize) {
return [rect];
}
let a: Rectangle;
let b: Rectangle;
// 縦横長い方を分割する
// 分割する際、領域の最低サイズさえ守ればどこから分割しても構わない
if (r.height(rect) >= r.width(rect)) {
// 縦長なので横に分割する
// 現在のサイズから領域2つと通路1マスを引いた余る、サイズを計算
const space = r.height(rect) - splitRectSize;
// 上の領域のサイズ(下端位置)を計算
// 領域の最低サイズ+余っているサイズをランダムに不可
const aBottom = rect.top + (minPartitionSize - 1) + rangeInt(0, space);
a = r.init(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, aBottom);
// 下の領域の上端位置はは上の領域から通路を挟んだ2つ下。
b = r.init(rect.left, aBottom + 2, rect.right, rect.bottom);
} else {
// 横長なので縦に分割する
// アルゴリズムは上記と同じ
const space = r.width(rect) - splitRectSize;
const aRight = rect.left + (minPartitionSize - 1) + rangeInt(0, space);
a = r.init(rect.left, rect.top, aRight, rect.bottom);
b = r.init(aRight + 2, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom);
}
// 分割したa, bを更に分割するために再帰呼び出しをする
// これ以上分割できないRectangleが[rect]という形で返却されるので、Array#concatで統合する
return splitRect(a).concat(splitRect(b));
}
引数で渡した矩形領域を再帰的に分割する。
領域 2 つの最低サイズと通路用の 1 マス分が確保できれば分割ができ、縦横とも分割できるならば長い方を分割する。
分割する位置は領域の最低サイズさえ確保できればどこから分割しても構わない。
矩形領域からの部屋作成
const minRoomSize = 4;
function createRoom(rect: Rectangle): Rectangle {
// 部屋のサイズを決定
const width = minRoomSize + rangeInt(0, r.width(rect) - minRoomSize - 2);
const height = minRoomSize + rangeInt(0, r.height(rect) - minRoomSize - 2);
// 部屋の左上位置を決定
const startX = rect.left + 1 + rangeInt(0, r.width(rect) - width - 2);
const startY = rect.top + 1 + rangeInt(0, r.height(rect) - height - 2);
// 部屋情報を返却
return r.init(startX, startY, startX + width - 1, startY + height - 1);
}
矩形領域の外側 1px を除いて、内部にランダムな大きさの部屋を作る。
つまり縦横ともに 2px 引いた値が最大サイズになる。
部屋の最低サイズは前もって用意しておいた定数 minRoomSize を参照する。
部屋を通路で繋ぐ
function makeCorridor(partitions: Rectangle[], rooms: Rectangle[]): void {
for (let i = 0; i < partitions.length - 1; i++) {
connect(partitions[i], partitions[i + 1], rooms[i], rooms[i + 1]);
}
for (let i = 0; i < partitions.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 2; j < partitions.length; j++) {
if (
partitions[i].left - 1 === partitions[j].right + 1 ||
partitions[i].right + 1 === partitions[j].left - 1 ||
partitions[i].top - 1 === partitions[j].bottom + 1 ||
partitions[i].bottom + 1 === partitions[j].top - 1
) {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
connect(partitions[i], partitions[j], rooms[i], rooms[j]);
}
}
}
}
}
function connect(
part0: Rectangle,
part1: Rectangle,
room0: Rectangle,
room1: Rectangle
): void {
let posA: number;
let posB: number;
// 縦に分割している場合
if (part0.bottom + 1 == part1.top - 1) {
posA = room0.left + rangeInt(0, r.width(room0) - 1);
posB = room1.left + rangeInt(0, r.width(room1) - 1);
fill(
r.init(posA, room0.bottom + 1, posA, part0.bottom + 1),
CellType.corridor
);
fill(r.init(posB, room1.top - 1, posB, part1.top - 1), CellType.corridor);
fill(
r.init(posA, part0.bottom + 1, posB, part1.top - 1),
CellType.corridor
);
}
// 横に分割している場合
else if (part0.right + 1 == part1.left - 1) {
posA = room0.top + rangeInt(0, r.height(room0) - 1);
posB = room1.top + rangeInt(0, r.height(room1) - 1);
fill(
r.init(room0.right + 1, posA, part0.right + 1, posA),
CellType.corridor
);
fill(r.init(room1.left - 1, posB, part1.left - 1, posB), CellType.corridor);
fill(
r.init(part0.right + 1, posA, part1.left - 1, posB),
CellType.corridor
);
}
}
部屋と部屋を繋ぐ通路を作成する。
splitRect() で、縦に分割する際、
- 上の領域を配列の左側
- 下の領域を配列の右側
横に分割する際、
- 左の領域を配列の左側
- 右の領域を配列の右側
に入れている。
これによって、
- 配列要素の隣同士の領域は縦か横で接触している
という事がわかる。
// 縦に分割している場合
if (part0.bottom + 1 == part1.top - 1) {
// ...
}
// 横に分割している場合
else if (part0.right + 1 == part1.left - 1) {
// ...
}
縦か横、どちらに接触しているかは位置を見て判定することができる。